After reading this paper, you’ll learn how to:
 Despite the massive amounts of data that companies have at their fingertips, few companies know how to make smart decisions using business analytics. Even fewer succeed at connecting information with decision-making. Instead of basing important decisions on facts, too many managers rely on their intuition, their experience or anecdotal evidence.
Despite the massive amounts of data that companies have at their fingertips, few companies know how to make smart decisions using business analytics. Even fewer succeed at connecting information with decision-making. Instead of basing important decisions on facts, too many managers rely on their intuition, their experience or anecdotal evidence.
The business data analysis enabled by business analytics and business intelligence software provides a critical competitive edge to firms. Yet a study indicates that enterprises don't fully understand the importance of these key apps. Almost a third of technology executives and business professionals say they don't know whether their organization uses business analytics or if their organizations have business analytics capabilities at all, according to new data from accounting and consulting giant Deloitte.3
Business analytics empowers you to take Better Decisions and Right actions.. It improves performance in Key Business domains using data and analysis. Combining the science of quantitative analysis with the art of sound reasoning, Business Analytics provides a roadmap and tools for unleashing the potential buried in your company’s data.
Business Analytics includes both:
Benefits of Business Analysis
Analytics can help to transform just about any part of your business or organization:
Customer relationships use analytics to segment their customers and identify their best ones. They analyze data to understand customer behaviors, predict their customers’ wants and needs, and offer fitting products and promotions. They price products for maximum profitability at levels that they know their customers will pay. Finally, they identify the customers at greatest risk of attrition and intervene to try to keep them.
Supply chain and operations optimize inventory levels and delivery routes, for example. They also segment their inventory items by cost and velocity, build key facilities in the best locations, and ensure that the right products are available in the right quantities.
Human resources, a traditionally intuitive domain, increasingly uses analytics in hiring and employee retention. Just as sports teams analyze data to pick and keep the best players, firms are using analytical criteria to select valuable employees and identify those who are most likely to depart.
Finance and accounting: Instead of just putting financial and non-financial metrics on scorecards, leading firms are using analytics to determine which factors truly drive financial performance. In this era of instability, financial and other firms are using analytics to monitor and reduce risk.
Stages in developing Analytical Capabilities of an Organization
The organizations have to go through 5 stages in developing their analytical capabilities. This ranges from analytically impaired to analytical competitors.
Organizations are struggling to understand how analytics can help them improve business results — and managers don’t even feel they have the time to figure it out. There are also cultural impediments around the organizational ownership and sharing of data. One interesting data point here is the perceived lack of skills. Our initial findings suggest that many organizations may have unrecognized talents within their midst — employees who consider themselves at least proficient in the use of analytics, but who are only occasionally asked to use them — especially in low-performing organizations.
Observations by MIT (Ref# 5)
References
- Use data more effectively and gain valuable analytical insights
- Manage and coordinate data, people, and technology at an enterprise level
- Understand and support what analytical leaders do
- Evaluate and choose realistic targets for analytical activity
- Recruit, hire, and manage analytical talent
- Click here to know on 'Analytics in SAP'
 Despite the massive amounts of data that companies have at their fingertips, few companies know how to make smart decisions using business analytics. Even fewer succeed at connecting information with decision-making. Instead of basing important decisions on facts, too many managers rely on their intuition, their experience or anecdotal evidence.
Despite the massive amounts of data that companies have at their fingertips, few companies know how to make smart decisions using business analytics. Even fewer succeed at connecting information with decision-making. Instead of basing important decisions on facts, too many managers rely on their intuition, their experience or anecdotal evidence.The business data analysis enabled by business analytics and business intelligence software provides a critical competitive edge to firms. Yet a study indicates that enterprises don't fully understand the importance of these key apps. Almost a third of technology executives and business professionals say they don't know whether their organization uses business analytics or if their organizations have business analytics capabilities at all, according to new data from accounting and consulting giant Deloitte.3
Business analytics empowers you to take Better Decisions and Right actions.. It improves performance in Key Business domains using data and analysis. Combining the science of quantitative analysis with the art of sound reasoning, Business Analytics provides a roadmap and tools for unleashing the potential buried in your company’s data.
Business Analytics includes both:
- Analysis of past, present, and projected future outcomes using advanced analytics
- Decision optimization for determining which actions will drive the optimal outcomes, and then delivering those recommended actions to the systems or people that can effectively implement them
- Business Analytics = Advanced Analytics + Decision Optimization
- Statistics Scoring Techniques
- Data Mining Rules Formulation
- Text Mining Recommendation Procedure
- Visualization Opmization Techniques
- Reporting
Advanced analytics are used to examine the way in which specific business issues relate to data on past, present, and projected future actions. Advanced analytics include statistical, mathematical, and other algorithmic techniques.
From this advanced analysis results insight that is used to determine which actions will drive the optimal outcomes. Recommended actions, along with supporting information, are delivered to the systems or people that can effectively implement them.Benefits of Business Analysis
- Help manage and steer business in turbulent times. Analytics give manager a tool to understand the dynamics of their business including how economic and marketplace shifts influence business performance
- Know what really is working. Rigorous analytical testing can establish whether your intervention is causing the desired changes in your business or whether it is simply the random statistical fluctuations
- Leverage previous investments in IT and information to get more insight, faster execution and more Business Value in many Business processes
- Cuts costs and improves efficiency. Optimization Technique can minimize asset requirements and predictive models can anticipate market shifts and enable companies to move quickly to slash costs and eliminate wastes
- Manage Risk. Greater Regulatory oversight will require more precise matrics and risk management model
- Anticipate changes in market environment . You can detects patterns in vast amount of customers and Market Data coming your way
- Have a basis of improving decisions over time. If you are using clear logic and explicit supporting data to make a decision, you or someone else can examine the decision process more easily and try to improve it.
Where do business analytics apply in an organization? 4
Analytics can help to transform just about any part of your business or organization:
Customer relationships use analytics to segment their customers and identify their best ones. They analyze data to understand customer behaviors, predict their customers’ wants and needs, and offer fitting products and promotions. They price products for maximum profitability at levels that they know their customers will pay. Finally, they identify the customers at greatest risk of attrition and intervene to try to keep them.
Supply chain and operations optimize inventory levels and delivery routes, for example. They also segment their inventory items by cost and velocity, build key facilities in the best locations, and ensure that the right products are available in the right quantities.
Human resources, a traditionally intuitive domain, increasingly uses analytics in hiring and employee retention. Just as sports teams analyze data to pick and keep the best players, firms are using analytical criteria to select valuable employees and identify those who are most likely to depart.
Finance and accounting: Instead of just putting financial and non-financial metrics on scorecards, leading firms are using analytics to determine which factors truly drive financial performance. In this era of instability, financial and other firms are using analytics to monitor and reduce risk.
Stages in developing Analytical Capabilities of an Organization
The organizations have to go through 5 stages in developing their analytical capabilities. This ranges from analytically impaired to analytical competitors.
- The capabilities required for any organization to become more analytical : “D.E.L.T.A.” model.
- Data: This is a pre-requisite for Analytics.
The data must be - Clean
- Common
- Integrated
- Accessible in a central data warehouse
“Collect data in areas that others haven’t addressed and then apply this data analytically in decision making “ – Tom Davenport - Enterprise: To become more analytical, organizations must go beyond managing the data locally. Create enterprise-wide analytical capabilities and invest in enterprise-scale analytical technologies.
- Leadership : The most important but extreme rare trait of analytical organizations. The leadership is required to develop and maintain ‘fact based decision making’ culture in the organization.
- Targets : With limited resources, the organizations have to pick a primary strategic target (e.g. supply chain) for their analytical efforts with a secondary target.
- Analysts : The analytical talent required include
- Champions : Who lead analytical initiatives (1% of the analytical organization)
- Professionals : Who can create new algorithms (5-10%)
- Semi-professionals : Who can use visual and basic statistical tools (15-20%)
- Amateurs : Who use spreadsheets (70-80%)
- Analytical Organization needs each type of individual
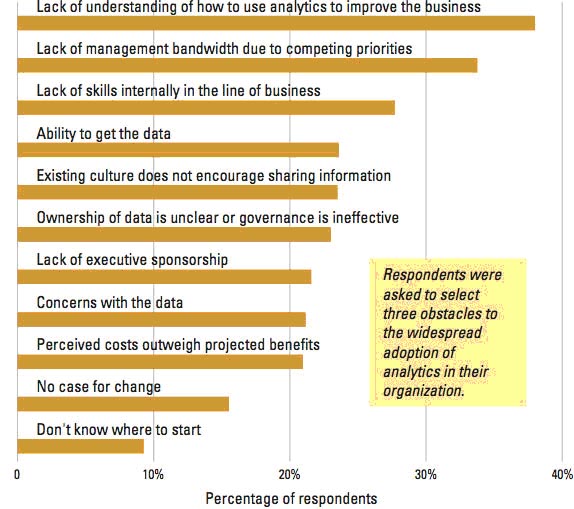
Obstacles for Adopting Analytics?
Organizations are struggling to understand how analytics can help them improve business results — and managers don’t even feel they have the time to figure it out. There are also cultural impediments around the organizational ownership and sharing of data. One interesting data point here is the perceived lack of skills. Our initial findings suggest that many organizations may have unrecognized talents within their midst — employees who consider themselves at least proficient in the use of analytics, but who are only occasionally asked to use them — especially in low-performing organizations.

Observations by MIT (Ref# 5)
References
Ref:
- Harvard Business Review Webinars - Analytics at Work: How to Make Better Decisions and Get Better Results http://blogs.hbr.org/events/HBR_Webinar_Davenport_Feb_2_10.pdf
- http://www.spss.com/predictive_analytics/work.htm
- http://itmanagement.earthweb.com/entdev/article.php/3900786/Study-Firms-Lack-Business-Analytics-Benefits.htm
- https://microsite.accenture.com/analyticsatwork/Documents/Accenture_analytics_at_work.pdf
- http://sloanreview.mit.edu/the-magazine/articles/2010/fall/521150/10-data-points-information-and-analytics-at-work/